Infectious is about 2.5 times that of influenza! This virus has entered a period of high incidence, and experts warn ↘.
Mycoplasma pneumonia, COVID-19, A stream, B stream …
near future
Many people are "hit" by various respiratory viruses.
November 22nd.
# Syncytial Virus # ranks first in Weibo Hot Search.
Some netizens asked, "What is this!"
Syncytial virus
It’s not a new respiratory disease
It has already appeared this summer.
An out-of-season epidemic

With the coming of winter, the temperature drops, and syncytial virus enters the high-incidence season. Wang Quanyi, deputy director of the Beijing Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention and chief expert of epidemiology, said that in Beijing, mycoplasma pneumoniae is not the first cause of pediatric visits, and the top three are influenza, adenovirus and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Syncytial virus rose to the third place.
Gao Weiwei, chief physician of neonatal respiratory department of Guangdong Maternal and Child Health Hospital, said that syncytial virus infection is the first cause of hospitalization of infants under 1 year old, and 95% of children may have been infected with syncytial virus before 2 years old. In the high epidemic season, more than 80% of infants’ acute lower respiratory tract infections are caused by syncytial virus infection.
What are the typical symptoms?
Who should pay special attention to?
How to effectively prevent it?
Spread through droplets and close contact
Children and adults can be infected.
▼
Syncytial virus is an RNA virus, which is transmitted by droplets and close contact, or by contaminated hands and objects. Patients often have upper respiratory symptoms after infection.
The incubation period of syncytial virus is usually 2-8 days, and detoxification can last for 1-3 weeks. Early infection is mostly confined to the upper respiratory tract, showing symptoms of upper respiratory tract such as nasal congestion, runny nose, cough and hoarseness.
The typical symptoms of children infected with syncytial virus are fever, cough, stuffy nose and runny nose.
The typical symptoms of adult infection are very similar to the common cold, such as low-grade fever, cough, stuffy nose and runny nose.
Most patients’ symptoms will disappear spontaneously within 1-2 weeks, and a small number can develop into lower respiratory tract infection (i.e. bronchiolitis or pneumonia), which is more common in young infants. Clinical symptoms include cough and wheezing.
Syncytial virus is about 2.5 times as contagious as influenza.
Infection among older children has increased this year.
▼
Gao Weiwei, chief physician of neonatal respiratory department of Guangdong Maternal and Child Health Hospital, said that syncytial virus is about 2.5 times as contagious as influenza. If children are seriously infected with syncytial virus at the age of 0-1, it may have a serious impact on their lung function, even for a long time.
Syncytial virus, like Covid-19 virus and influenza virus, spreads through respiratory tract, causing respiratory symptoms such as fever, cough, stuffy nose and runny nose, but there are some differences.
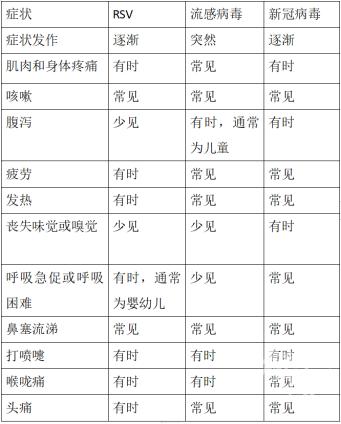
Similarities and differences of three viruses. Source: Popular Science China
It is reported that respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in southern China experienced a wave of epidemic peak this year. After a short decline, it rose again as the temperature dropped. For children, RSV and influenza are easy to attack in groups. Moreover, respiratory syncytial virus mostly occurred in children younger than 2 years old in previous years, and the infection of older children has increased this year.
There are no vaccines and specific treatments.
Repeated infection, prone to family transmission.
▼
At present, there are no syncytial virus vaccines and special therapeutic drugs on the market in China. Syncytial virus can be repeatedly infected, and it is also prone to family transmission. In the absence of vaccines and effective drugs, measures such as strengthening personal protection should be taken to prevent infection:
In the epidemic season of syncytial virus, try to avoid going to crowded places;
Wear a mask when going out, and pay attention to cover when sneezing;
Pay attention to hand hygiene, do not touch, wash your hands frequently;
Personal protection should be done in medical institutions to prevent cross-infection in hospitals.

Xinhua news agency data map
Except syncytial virus
Pay special attention to influenza virus in the near future.
The incidence of influenza in Guangdong has increased significantly since September.
▼
On November 23rd, the latest weekly influenza surveillance report released by the National Influenza Center showed that the proportion of influenza-like cases in sentinel hospitals in southern provinces reached a new high in the past three months, reaching 6.4%, which was higher than that in northern provinces (6.2%). About 30% of influenza-like cases were tested positive, and the positive rate of influenza in southern provinces was higher than that in northern provinces.
According to the notification of infectious diseases in Guangdong Province, the number of influenza cases in Guangdong has increased significantly since September, reaching a new high in the past six months in October. Guangdong CDC issued a document four times recently, calling on the public to actively vaccinate against influenza.

Dry weather is conducive to the survival and spread of influenza virus.
Ying Qin washes his hands and wears a mask to get the flu vaccine.
▼
@ Guangdong Weather Release Reminder: It is expected that in the next few days, Guangdong will still maintain dry weather, and low humidity is conducive to the survival and spread of influenza virus. How to avoid children’s respiratory tract infection?
Experts generally suggest that you should wear masks in public places, try to avoid going to crowded places, wash your hands frequently, drink plenty of water, have more ventilation, and get the flu vaccine as soon as possible.
Yin Genquan, deputy director of the internal medicine department of Guangzhou Women and Children Medical Center and chief physician of the respiratory department, also said that from the perspective of increasing children’s resistance, the best "medicine" is four words: correct care, comprehensive nutrition, proper exercise and happy mood.

Children with mild symptoms can consider home observation.
Avoid cross infection
▼
At the peak of pediatric visits, Yang Jinghua, director of the Pediatrics Department of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, suggested that if older children have mild symptoms, good mental state and no obvious refusal to eat or drink, they can consider home observation to reduce the risk of cross-infection when seeking medical treatment. However, please take your child to see a doctor in time in the following situations:
Infants under 3 years old have fever and cough.
High fever persists.
Repeated fever cannot be relieved for more than 2-3 days.
Poor mental state, listlessness, lethargy
Severe cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, etc.
Mo Xiaolan, deputy director and chief pharmacist of the Pharmacy Department of Guangzhou Women and Children Medical Center, said that no matter what kind of pathogen is infected, the general principle of medication for children with acute upper respiratory tract infection is to rest, drink plenty of water and deal with symptoms. "If you don’t use drugs, you don’t use drugs. If you can use only one drug, you don’t need multiple drugs. If you can take it orally, you don’t need intravenous infusion."
Are there many people around you who have a cold and fever recently?
Forward it to your relatives and friends to remind each other!
Original title: "Infectious is about 2.5 times that of influenza! This virus has entered a period of high incidence, experts remind ↘ "
Read the original text