It is a matter of health, beware of these infectious diseases!
Recently, the Hunan Provincial Health and Health Commission and the Hunan Provincial Department of Education issued the Notice on Strengthening the Prevention and Control of Key Infectious Diseases in Schools in Autumn and Winter. Infectious diseases on campus mainly spread through respiratory tract in autumn and winter, and some spread through digestive tract and contact, so it is easy to break out and spread in campus, so we should pay special attention to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
According to the epidemic situation and incidence characteristics of infectious diseases, the school hospital has sorted out several knowledge of prevention and treatment of common infectious diseases in autumn and winter, please pay attention to it!
I. Influenza

(A) disease science
Influenza is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza virus, and it is also a highly contagious and fast-spreading disease. Fog droplets ejected mainly by coughing or sneezing of infected people are transmitted to others through the air, and can also be infected by touching objects contaminated by influenza virus. The main clinical manifestations are high fever, headache, limb aches, fatigue and upper respiratory symptoms such as runny nose and cough. The infirm and the elderly are prone to pneumonia and other complications after infection.
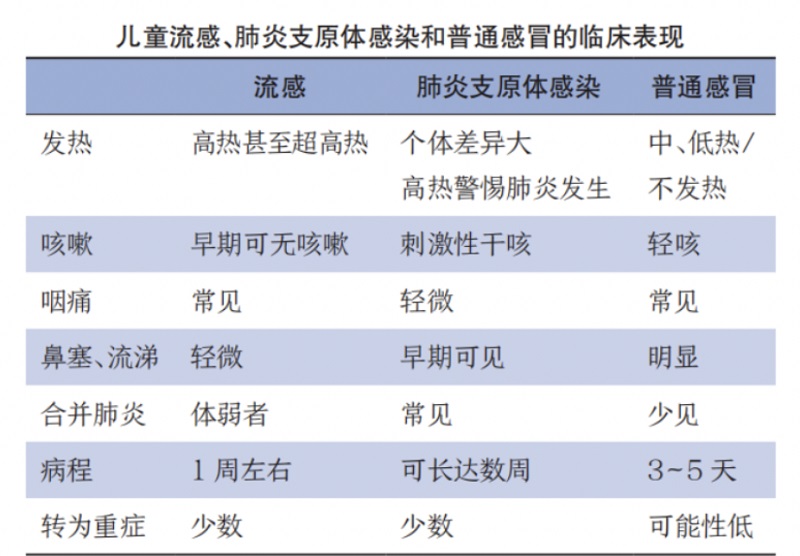
The difference between influenza and common cold
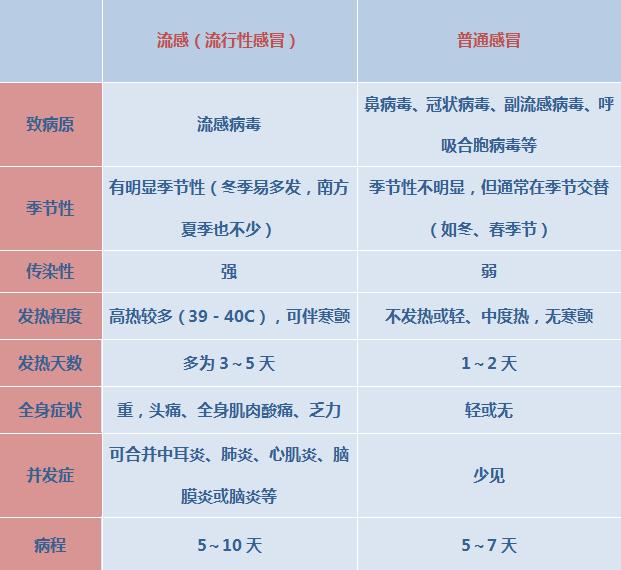
(2) Prevention and control suggestions
1. Before the flu season, it is an effective way to prevent the flu by vaccinating high-risk groups and susceptible groups.
2. Reasonable arrangement of work and rest time: have a regular life, ensure adequate sleep, and avoid the decline of resistance caused by overwork, thus increasing the chance of illness.
3. Pay attention to personal hygiene: don’t spit everywhere, and cover your mouth and nose with a handkerchief or paper towel when sneezing or coughing.
Wash your hands frequently, and wash your hands immediately after touching respiratory secretions (such as after sneezing).
4. Open the window and ventilate several times a day to keep the indoor air fresh. During the high incidence of influenza, try not to go to crowded places with dirty air; You’d better wear a mask when you have to.
5. Effective prevention approaches: early detection, early reporting, early isolation and early treatment. Isolating patients is the most effective way to reduce transmission.
Second, cold diarrhea

(A) disease science
Infectious diarrhea refers to diarrhea caused by intestinal infection of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. Its prevalence is wide, the incidence rate is high, it has the characteristics of acute onset, rapid spread and wide coverage, and it is an important disease that harms health. Mostly due to the intake of unclean diet (such as cold dishes, spoiled shrimp, crabs, drinks, etc.) and water, due to bacterial and viral pollution, coupled with some people’s bad hygienic eating habits, the disease enters the mouth. The clinical manifestation is diarrhea, which may be accompanied by abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms. The stool characteristics often vary with different pathogens, and in severe cases, fever, dehydration, electrolyte disorder, abnormal renal function, acidosis, shock and so on may occur. Infectious diarrhea pathogens are excreted with excreta, which pollutes the environment, food and water sources and can cause outbreaks.

(2) Prevention and control suggestions
1. Pay attention to drinking water hygiene, don’t drink raw water, don’t eat cold and spoiled food, especially seafood and aquatic products.
2. Pay attention to food hygiene, don’t overeat, and eat less food that is easy to carry germs and be bitten by flies; Tableware should be disinfected, and raw and cooked tableware should be separated; Try to eat cooked food, and wash and peel raw fruits and vegetables.
3. Pay attention to personal hygiene, wash your hands before and after meals, do not defecate anywhere, do not dump garbage and dirt, and do not pollute water sources.
4. Report the patients with vomiting and diarrhea in time, and see a doctor as soon as possible for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Third, tuberculosis

(A) disease science
Tuberculosis, also known as "consumption", is a chronic infectious disease caused by the infection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (commonly known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis). The part often invaded by Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the lung, which is called tuberculosis. The clinical manifestations of tuberculosis are various, and the early symptoms are mild and atypical. It is easy to be confused with other respiratory diseases, such as tracheitis and pneumonia, and it is often ignored, which leads to the delay of medical treatment. Cough, expectoration, hemoptysis or bloodshot sputum are the main symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis. Most patients with pulmonary tuberculosis have hemoptysis with blood in sputum, and a few patients have hemoptysis with big mouth. In addition, chest tightness, chest pain, low fever in the afternoon, night sweats, general weakness, loss of appetite or weight loss are also common symptoms of tuberculosis.
(2) Prevention and control suggestions
1. Take tuberculosis examination as a compulsory item for physical examination of teachers and students.
2. Do not spit everywhere, cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and wear a mask to reduce the spread of tuberculosis.
3. After suspicious symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis appear or are diagnosed as pulmonary tuberculosis, you should take the initiative to report to the school, and don’t hide your illness or attend classes with illness.
4. Develop the habit of frequently opening windows for ventilation; Do a good job in campus environmental sanitation, and eliminate the dead corner of sanitation.
5. Ensure adequate sleep, reasonable diet, strengthen physical exercise and improve the ability to resist diseases.
Fourth, dengue fever
(A) disease science
Dengue fever is an acute mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by the spread of dengue virus through mosquito bites. Dengue fever has the characteristics of typical importation, suddenness, rapid spread, high incidence, general susceptibility of the population and high mortality of a few severe cases. The clinical features are sudden onset, high fever (sometimes up to 39℃), general muscle pain, joint pain, extreme fatigue, and some patients may have rash, bleeding tendency and lymph node enlargement. At present, the epidemic situation of dengue fever in Southeast Asia, South America, Africa and other places is more serious, and cases of dengue fever have appeared in Yunnan, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Hainan and other regions in China. At present, there are no vaccines and specific therapeutic drugs that can prevent the disease. The focus of treatment is to control pain with painkillers, usually acetaminophen (paracetamol).
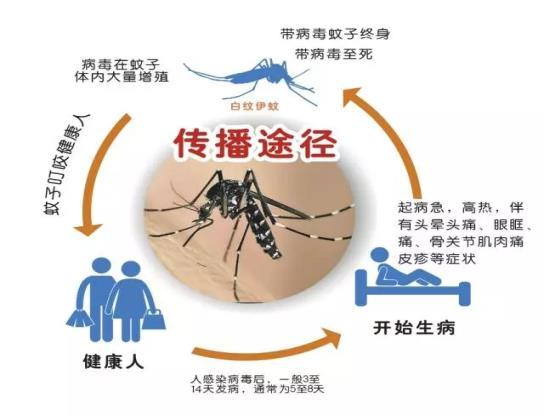
(2) Prevention and control suggestions
Avoiding being bitten by mosquitoes is the key. Try to choose light-colored long-sleeved trousers and use mosquito repellent or other mosquito repellent drugs when going out.
2. Screen windows and screen doors should be installed in the residence. You can use mosquito-repellent incense, mosquito-repellent aerosol, etc. in the hotel room before going out. Even in high-end hotels, you should pay attention to indoor mosquito killing. Avoid staying in the dark and humid outdoors such as grass, shade and gazebo for a long time.
3. If symptoms appear, see a doctor in time. If you come back from dengue endemic areas (Yunnan, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Fujian and other domestic endemic areas, Southeast Asia, South America, Africa and other overseas endemic areas), please pay attention to your own health observation. If you have a persistent high fever within 2 weeks, accompanied by symptoms such as headache, orbital pain, muscle and joint pain, nausea, vomiting, rash, etc., you should go to a regular hospital as soon as possible, and inform the doctor of his recent residence history and remind him that he may have dengue fever; When staying at home or in hospital, do a good job in mosquito isolation (especially within 5 days after onset), including using mosquito nets, screen doors and screens, wearing long-sleeved underwear, spraying mosquito repellent and other measures to reduce unnecessary outdoor activities and prevent further spread.
V. Covid-19 infection
(A) disease science
At present, XBB series variants of Omicron subtype have become dominant in most provinces in China, and this trend is likely to continue in the future. The National Bureau of Disease Control and Prevention also said that the epidemic situation of COVID-19 in China is generally at a low level and in a wave-like fashion recently, and the epidemic situation has brought less pressure to local medical systems, so there will be no large-scale epidemic in the short term. However, it should be noted that cases of multiple infections with COVID-19 are more common. Through the search, we can find that the number of COVID-19-infected outpatients in hospitals has increased recently, and most patients are infected with Covid-19 or influenza virus.

(2) Prevention and control suggestions
1. Actively vaccinate. Elderly people aged 60 and above, people aged 18-59 with serious basic diseases, people with low immune function, people with high risk of infection, and people who have completed basic immunization or have been infected with Covid-19 should be actively vaccinated to further strengthen their autoimmune ability.
2. Pay attention to personal protection. Residents should wear masks in their daily trips, minimize unnecessary gatherings and keep social distance. Maintain good personal and environmental hygiene, wash hands frequently, often ventilate, pay attention to rest, pay attention to nutrition and enhance physical fitness.
3. Use drugs rationally and see a doctor as needed. After infection, residents should take corresponding treatment measures according to the severity of their own symptoms, implement self-care at home, reduce contact with their roommates, rationally use symptomatic drugs according to relevant guidelines, do a good job in health monitoring, and go to medical institutions in time if the condition worsens.
Six, monkeypox
(A) disease science
Monkeypox (Mpox) is a viral zoonotic infectious disease caused by Mpox virus. The main clinical manifestations are fever, rash and lymphadenopathy. Recently, many provinces and cities in China reported cases of monkeypox. Monkeypox cases are mainly men who have sex with men. Recently, there have been some cases of infection among women and medical staff.
(2) Prevention and control suggestions
1. Pay close attention to the epidemic information of monkeypox in the local area or travel destination in time to avoid direct contact with wild animals in high-incidence countries. Avoid catching, slaughtering and eating local animals raw.
2. Good hygiene habits, frequent cleaning and disinfection, and good hand hygiene.
3. If you find sex with a rash (especially in genitals, perianal parts, etc.), avoid close contact with it. Using condoms can’t completely prevent monkeypox virus infection.
4. The interpersonal transmission of monkeypox is mainly among men who have sex with men. It is suggested that men who have sex with men actively understand the knowledge of monkeypox prevention to avoid or reduce high-risk behaviors.
5. If you have symptoms such as fever, rash and lymphadenopathy of unknown reasons, you should take the initiative to seek medical treatment.
Seven, dog injury
(A) disease science
Rabies is a zoonotic acute infectious disease. Once it breaks out, the mortality rate is close to 100%. According to the data released by the World Health Organization (WHO), rabies still kills 59,000 people worldwide every year, and one person dies of rabies every 9 minutes, and 99% of the cases are caused by dog bites. Main symptoms (rabies): fear of water, fear of wind, pharyngeal muscle spasm and progressive paralysis. Raising awareness of rabies prevention, vaccinating dogs and strengthening post-exposure treatment of human rabies in epidemic areas are the most effective rabies prevention measures at present, and it is also the global consensus on rabies prevention.

(2) Prevention and control suggestions
1. Pet dog owners must consciously raise dogs in accordance with the law, vaccinate cats and dogs, and use leashes when going out to avoid dogs hurting people and spreading rabies virus.
2. Rabies can be prevented and cured. If you are scratched or bitten by a dog/cat, even if the wound is small, you should not be careless. You should seek medical advice in time. It is recommended to go to a medical institution with relevant qualifications for treatment, and do a good job in handling rabies after exposure according to the wound condition and personal immunization history.
3. After being scratched or bitten by a dog/cat, the individual should give first aid: if the wound is deep, especially the bleeding wound, you should first press the wound with a clean cloth to stop bleeding, and then rush to the hospital; If the wound surface is shallow or bleeding is not much, you can first clean the wound with flowing water or soapy water for 15 minutes, then use a clean paper towel to absorb the residual liquid at the wound, and then cover the wound with a clean cloth and seek medical attention as soon as possible. In addition to preventing rabies, we should also guard against other wound infections, such as tetanus infection.
4. Old people and children should receive more protection. Because the elderly and children have weak self-protection ability and lack of awareness of risk prevention, the incidence of animal injuries is high.
Original title: "It is related to health, beware of these infectious diseases! 》
Read the original text





 1 "Jiangsu Province in 2022 college graduates" three supports and one support "recruitment schedule". xls
1 "Jiangsu Province in 2022 college graduates" three supports and one support "recruitment schedule". xls 2.2022 college graduates "three supports and one support" plan registration form and instructions for filling out the form. doc
2.2022 college graduates "three supports and one support" plan registration form and instructions for filling out the form. doc













